Questions
Conceptual
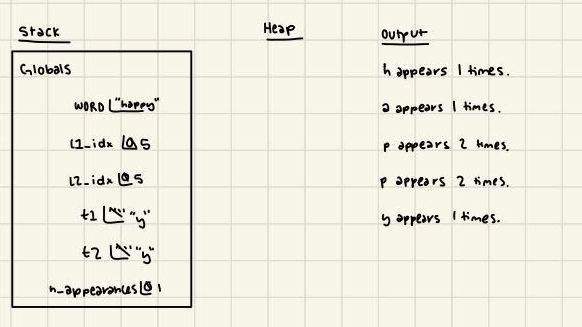
Produce a memory diagram for the following code snippet, being sure to include its stack and output.
WORD: str = "happy" l1_idx: int = 0 l2_idx: int = 0 t1: str = "" t2: str = "" n_appearances: int = 0 while l1_idx < len(WORD): t1 = WORD[l1_idx] n_appearances = 1 l2_idx = 0 while l2_idx < len(WORD): t2 = WORD[l2_idx] if (t1 == t2) and (l1_idx != l2_idx): n_appearances = n_appearances + 1 l2_idx = l2_idx + 1 print(f"{WORD[l1_idx]} appears {n_appearances} times.") l1_idx = l1_idx + 1
1.1 What would happen if while l1_idx < len(WORD) in line 8 was replaced with while l1_idx < len(WORD) - 1? Why?
1.2 What would happen if l2_idx=0 was moved to inside the second while loop? In other words, what if lines 11-13 were changed to:
while l2_idx < len(WORD):
l2_idx = 01.3 What would happen if, in line 16, if (t1 == t2) and (l1_idx != l2_idx): was replaced with if (t1 == t2):? Why?
1.4 What would happen if line 18 (l2_idx = l2_idx + 1) was removed? Why?
1.5. What would happen if the < symbol in line 8 was replaced with <=? (In other words, what if it was changed to while l1_idx <= len(WORD):)? Why?
- Consider the following code snippet:
x = 0
y = "hello"
while x < len(y):
print(y[x])
x += 1What will be the outcome of this code? The commas indicate a new line.
- “h”, “e”, “l”, “l”, “o”
IndexError: list index out of range
- The loop will run infinitely.
- No output (the code contains an error)
- What happens if the condition of a
whileloop is initiallyFalse?
- The loop will run once.
- The loop will not run at all.
- The loop will run infinitely.
- The loop will throw an error.
- What must the condition evaluate to for the following
whileloop to execute at least once?
while 3 + 3 != 4 + 5.6: True
False
true
false
None
Solutions
Conceptual Solutions
- Here’s a link to a video of the solution!
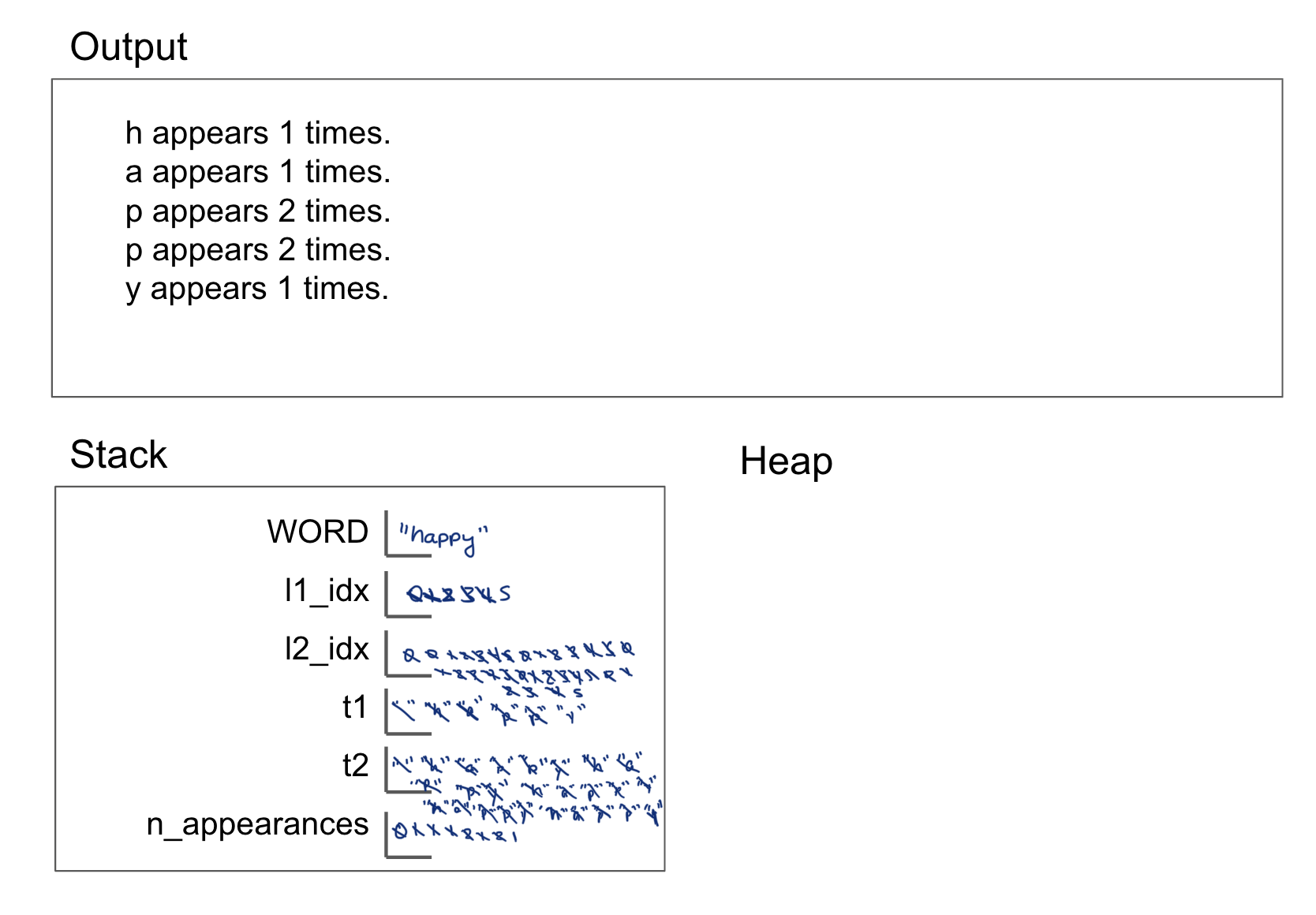
(We do not require that you write out all interim values as long as the initial and final values are correct like in the solution below. However, writing the interim values will help for practice purposes and to avoid mistakes!)
1.1 “y appears 1 times.” would not print. This is because l1_idx will not enter the while loop for l1_idx = 4. (For more practice, it’d be good to diagram this instance out to see how it would impact the final values of other variables.)
1.2 An infinite loop would occur because l2_idx would always equal 1 when returning to the top of the loop, and therefore l2_idx < len(WORD) will always be True.
1.3 If l1_idx != l2_idx is no longer required, this means that each letter can count itself twice. For example, WORD[0] == WORD[0] is true, so n_appearances for "h" would increase to 2.
1.4 There would be an infinite loop because l2_idx will never increase, and therefore l2_idx < len(WORD) will always be True.
1.5 There would be an index error because there would be the case where l1_idx = 5, so on line 9 WORD[5] would be searching for the element at index 5 in "happy", when the indexes only go up to 4.
c. The loop will run infinitely. This is because
x += 1is outside the loop, soxwill never increase within the loop, causing an infinite loop.b. The loop will not run at all. If the condition is initially
False, the loop will skip entirely.a. True. The condition must evaluate to
Truefor the loop to execute at least once. In this case, the condition3 + 3 != 4 + 5.6is always true, so the loop will run.